Retirement age determination is a complex process that varies significantly across different countries and pension systems worldwide. Understanding how retirement age is calculated is essential for effective financial planning and ensuring a secure retirement future. This comprehensive guide explores the various methodologies, factors, and considerations that influence retirement age calculations globally.
What Is Retirement Age?
Retirement age refers to the age at which individuals become eligible to receive full retirement benefits from government pension systems or social security programs. This age threshold represents a crucial milestone in workforce planning and financial security for millions of workers worldwide.
Key Factors in Retirement Age Determination
1. Birth Year
One of the most fundamental factors in retirement age calculation is an individual’s birth year. Many countries have implemented gradual increases in retirement age to address demographic challenges such as increased life expectancy and aging populations. These adjustments often follow a phased schedule:
- Earlier birth cohorts typically have lower retirement ages
- Later birth cohorts face progressively higher retirement ages
- Transition periods may span several decades to smooth the adjustment
2. Gender Considerations
Historically, many countries established different retirement ages for men and women, often allowing women to retire earlier. However, this practice is evolving:
- Traditional systems: Women could retire 2-5 years earlier than men
- Modern reforms: Many jurisdictions are equalizing retirement ages between genders
- Transition mechanisms: Gradual phase-ins help minimize disruption to retirement planning
3. Occupational Categories
Certain professions receive special retirement age provisions due to the nature of their work:
- Hazardous occupations: Mining, chemical industries, and high-risk manufacturing
- Physically demanding roles: Construction workers, maritime personnel
- Special civil service positions: Military personnel, law enforcement, firefighters
- Healthcare workers: Some systems provide earlier retirement for medical professionals
These workers often qualify for earlier retirement, sometimes 5-10 years before the standard age.
Types of Retirement Age
Normal Retirement Age (NRA)
The standard age at which workers become eligible for full, unreduced retirement benefits. This varies by country and system but typically ranges from 60 to 67 years.
Early Retirement Age
Many pension systems allow individuals to claim benefits before reaching normal retirement age, though this usually results in:
- Permanently reduced monthly benefits (typically 5-7% per year of early claiming)
- Minimum age thresholds (often 55-62 years)
- Specific eligibility criteria (such as minimum contribution years)
Deferred Retirement Age
Some systems incentivize working beyond normal retirement age by offering:
- Enhanced benefit amounts (often 5-8% per year of delay)
- Maximum age limits for accrual (typically 70-75 years)
- Flexible claiming options
Global Retirement Age Calculation Methods
Fixed Age Systems
The simplest approach establishes a specific retirement age for all citizens or specific demographic groups. While straightforward, this method lacks flexibility for individual circumstances.
Progressive Age Systems
More sophisticated systems adjust retirement age based on birth year cohorts, implementing gradual increases over time. This allows governments to respond to demographic changes while providing predictability for workers.
Service-Based Systems
Some countries incorporate years of service or contribution periods into retirement calculations:
- Minimum contribution years: Often 15-40 years required
- Early retirement with full service: May allow retirement before normal age if sufficient contributions made
- Combined age and service formulas: For example, “rule of 80” (age + service years = 80)
Life Expectancy-Linked Systems
Advanced systems automatically adjust retirement age based on population longevity trends, ensuring long-term sustainability of pension programs.
Regional Variations in Retirement Age
Europe
European countries generally maintain retirement ages between 65 and 67, with many implementing gradual increases to address demographic pressures. The European Union has seen convergence in retirement policies while respecting national sovereignty.
North America
- United States: Full retirement age ranges from 66 to 67 depending on birth year, with early retirement available at 62
- Canada: Standard age of 65 with flexibility from 60 to 70
- Mexico: Age 65 for most workers with varying requirements by social security regime
Asia-Pacific
This region shows considerable diversity:
- Developed economies (Japan, South Korea, Singapore): Ages 65-67 with ongoing increases
- Emerging economies: Often lower retirement ages (55-60) with reform initiatives underway
- Developing nations: Varied systems with limited coverage
Latin America
Latin American countries typically set retirement ages between 60 and 65, with ongoing pension reforms addressing sustainability concerns.
Africa and Middle East
These regions exhibit the widest variation, ranging from 55 to 65, often influenced by economic development levels and social structures.
Special Calculation Considerations
Contribution Requirements
Beyond age, many systems require minimum contribution periods:
- Full pension eligibility: Often 30-40 years of contributions
- Partial pension rights: May require 10-15 years minimum
- Credit for non-working periods: Some systems credit time for childcare, education, or unemployment
Health and Disability Provisions
Individuals unable to work due to health conditions may qualify for:
- Disability retirement at any age
- Reduced age thresholds for specific medical conditions
- Special assessment processes
Transitional Rules
When retirement age changes, governments typically implement transitional provisions to protect workers near retirement, including:
- Grandfathering older cohorts under previous rules
- Gradual phase-in schedules
- Enhanced benefits for affected transition groups
Planning for Retirement
Understanding your specific retirement age calculation is crucial for:
- Financial planning: Determining savings needs and investment timelines
- Career decisions: Planning potential career extensions or early exits
- Benefit optimization: Maximizing lifetime retirement income
- Healthcare preparation: Coordinating retirement with health coverage transitions
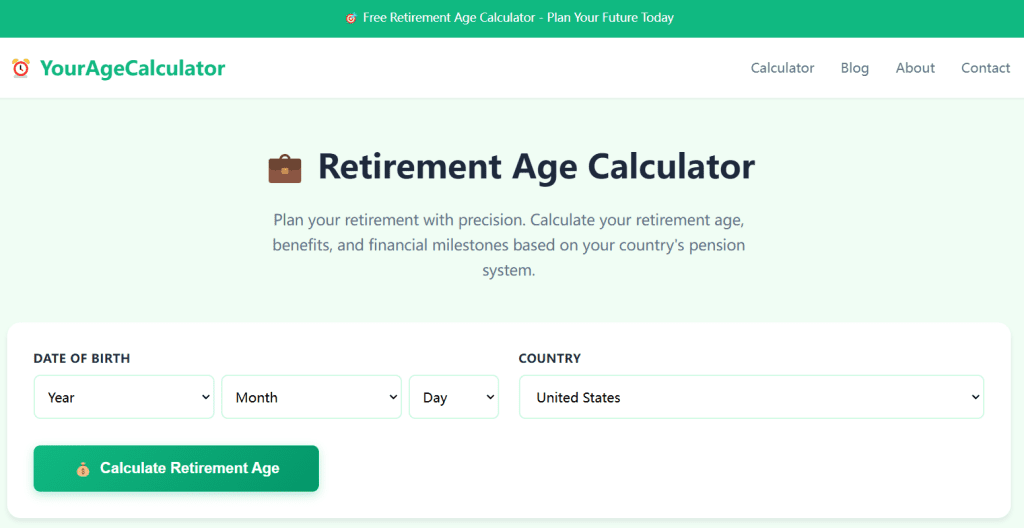
Using Retirement Age Calculators
Modern retirement age calculators provide personalized estimates by considering:
- Your specific birth date
- Country and applicable pension system
- Gender (where relevant)
- Occupational category
- Contribution history
- Special circumstances
These tools offer valuable guidance but should be complemented with official information from relevant pension authorities.
Future Trends in Retirement Age
Increasing Longevity Impact
As life expectancy continues to rise, more countries will likely:
- Increase standard retirement ages
- Implement automatic adjustment mechanisms
- Emphasize flexible retirement options
Workforce Dynamics
Changing employment patterns may influence retirement policies:
- Gig economy considerations
- Multiple career transitions
- Lifelong learning integration
Sustainability Concerns
Governments must balance:
- Pension system financial viability
- Adequate retirement security
- Intergenerational equity
- Labor market participation
Retirement age calculations represent a critical intersection of demographic, economic, and social policy considerations. While methodologies vary globally, the trend toward increased retirement ages reflects universal challenges of population aging and pension sustainability.
Understanding how your retirement age is determined empowers better planning and decision-making. Whether you’re decades from retirement or approaching this milestone, staying informed about applicable rules and calculation methods ensures you can optimize your retirement timing and benefits.
For personalized retirement age calculations specific to your situation, consult official sources from your national social security or pension authority, and consider using verified retirement calculators that account for your unique circumstances.
This guide provides general information about retirement age calculations worldwide. Specific rules and regulations vary by country and system. Always verify information with official government sources or qualified pension advisors for decisions affecting your retirement planning.